
The agricultural sector is experiencing a technological revolution, with innovations transforming traditional farming into a modern, efficient, and sustainable industry. With the global population projected to reach 9.7 billion by 2050, the demand for food is surging, making it essential to adopt advanced methods to increase productivity while minimizing environmental impact. This article explores some of the most promising innovations and technologies currently reshaping agriculture and helping farmers meet today’s challenges.
I. Precision Agriculture
Precision agriculture is one of the leading innovations in modern farming. This approach leverages technology to monitor and manage crops at a granular level, helping farmers make data-driven decisions. Key components of precision agriculture include:
1. GPS Technology: GPS-equipped tractors and farm machinery allow farmers to plant, irrigate, and fertilize with pinpoint accuracy, reducing waste and optimizing resource use.
2. Satellite Imaging and Drones: Satellites and drones provide aerial images of crops, enabling farmers to identify areas that need attention, such as sections affected by disease or pests. This technology helps in targeting specific areas, conserving resources and reducing the overall environmental impact.
3. Soil Sensors: Sensors placed in the soil measure moisture, pH levels, and nutrient content, providing real-time data that helps farmers make informed decisions about irrigation, fertilization, and planting.
By adopting precision agriculture, farmers can maximize yields, reduce input costs, and improve sustainability.
II. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning
AI and machine learning are revolutionizing agriculture by enabling data analysis on an unprecedented scale. Some of the major applications of AI in agriculture include:
1. Predictive Analytics: AI-powered tools analyze data on weather patterns, soil conditions, and crop health to predict potential problems and recommend timely interventions.
2. Automated Pest and Weed Control: Machine learning algorithms can detect weeds and pests in real time, allowing automated systems to apply herbicides or pesticides only where needed. This reduces chemical usage, lowering costs and environmental impact.
3. Robotic Harvesting: AI-driven robots are becoming capable of identifying ripe produce and performing complex tasks, such as picking fruits and vegetables, with greater efficiency than human labor.
AI-driven technologies improve decision-making, optimize productivity, and reduce labor costs, making agriculture more efficient and resilient.
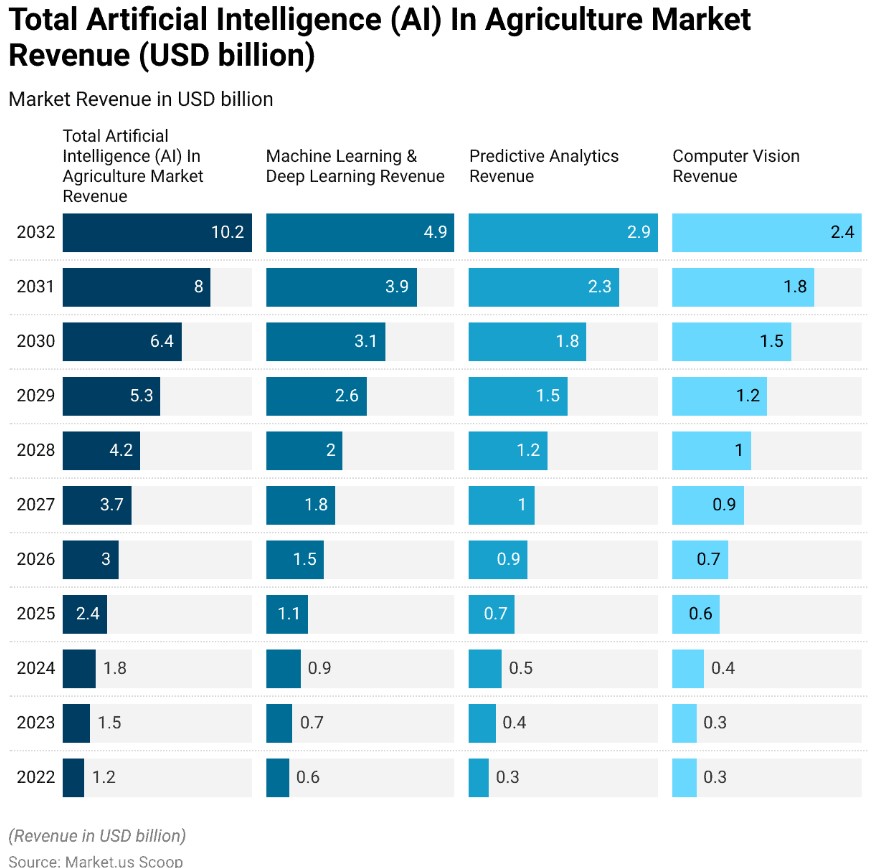
III. Internet of Things (IoT) in Agriculture
The Internet of Things (IoT) connects physical devices, allowing them to communicate and share data, which is particularly valuable in agriculture. IoT applications in farming include:
1. Smart Irrigation Systems: IoT-enabled sensors monitor soil moisture levels, weather forecasts, and crop water requirements, adjusting irrigation schedules automatically. This minimizes water waste and ensures crops receive the exact amount needed for optimal growth.
2. Livestock Monitoring: Wearable IoT devices for livestock track animal health, movement, and feeding patterns. This data helps farmers detect diseases early, monitor reproduction cycles, and improve overall herd management.
3. Climate Monitoring: IoT devices can track weather conditions, soil temperature, and humidity in real time. These insights help farmers anticipate and prepare for changes that could affect crop yield and quality.
IoT technology enhances real-time decision-making and resource management, leading to increased productivity and sustainability.
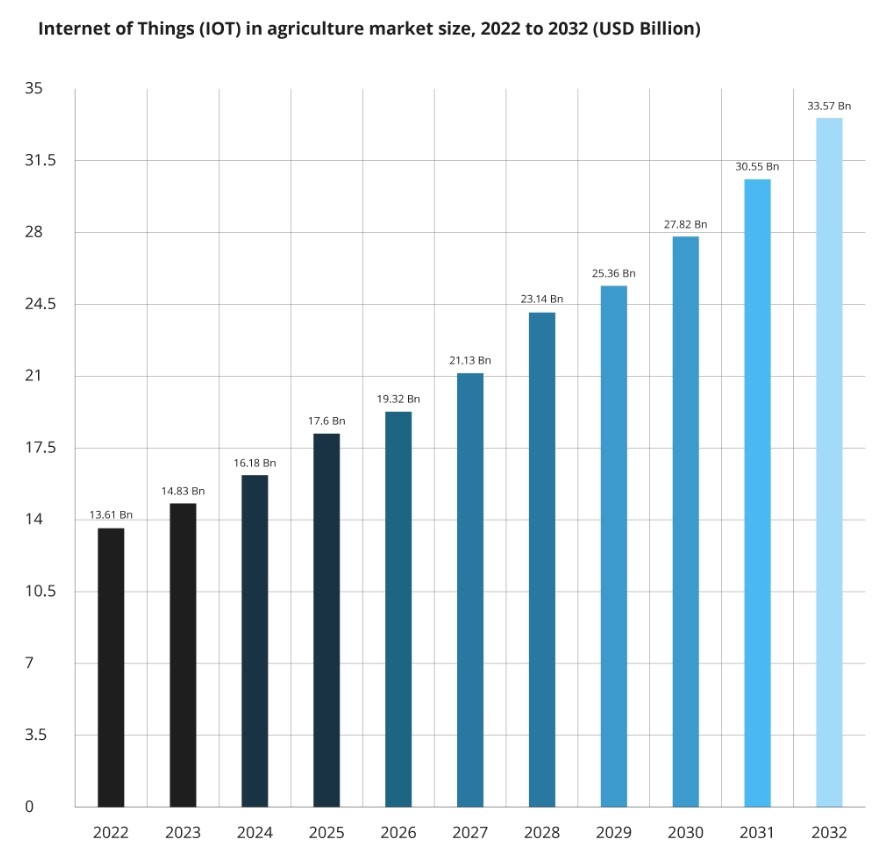
IV. 4. Vertical and Indoor Farming
Vertical farming and indoor agriculture are innovative solutions to the limitations of traditional farming, particularly in urban areas and regions with unsuitable climates. By growing crops indoors in stacked layers, vertical farming maximizes space usage and provides controlled conditions for optimal growth.
1. Hydroponics and Aeroponics: These soil-free farming techniques use nutrient-rich water or mist to grow plants, reducing the need for large plots of land and conserving water.
2. LED Lighting and Climate Control: Energy-efficient LED lights and advanced climate control systems create optimal growth conditions indoors, allowing farmers to grow crops year-round regardless of external weather.
3. Urban Agriculture: Vertical farming enables local food production in urban centers, reducing transportation costs and environmental impact while providing fresh produce to city dwellers.
Vertical and indoor farming provide a sustainable, space-efficient alternative to traditional agriculture, especially in densely populated areas or places with challenging climates.
V. CRISPR and Genetic Engineering
The advent of CRISPR (Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats) technology has revolutionized genetic engineering, allowing scientists to edit genes with precision. Applications of CRISPR in agriculture include:
1. Crop Improvement: Genetic editing can enhance crop resistance to pests, diseases, and environmental stressors like drought and salinity. This helps farmers maintain yields even in adverse conditions.
2. Enhanced Nutrition: CRISPR allows scientists to modify crops to improve nutritional content, such as developing rice with increased levels of vitamin A.
3. Faster Breeding: Genetic editing accelerates the breeding process, enabling farmers to bring improved crop varieties to market more quickly.
CRISPR and genetic engineering open up new possibilities for developing resilient, nutritious crops that can meet the needs of a growing global population.
VI. Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology, best known for its role in cryptocurrency, is making waves in agriculture by improving transparency, traceability, and security in the food supply chain. Applications in agriculture include:
1. Supply Chain Transparency: Blockchain allows every step of the supply chain to be documented, from farm to table. This helps consumers know where their food comes from and ensures fair practices for all stakeholders.
2. Food Safety: Blockchain records make it easier to trace contaminated products back to their source, reducing response times during food safety incidents.
3. Smart Contracts: Blockchain-based smart contracts enable automatic payments and contracts between farmers, suppliers, and buyers, improving efficiency and reducing the risk of disputes.
By increasing traceability and efficiency, blockchain fosters trust in the food system and promotes fair, ethical, and safe food practices.
VII. Biotechnology and Synthetic Biology
Biotechnology continues to push the boundaries in agriculture, creating new methods to enhance crop and livestock productivity. Synthetic biology, a branch of biotechnology, designs new biological systems or modifies existing ones. Examples of biotechnology in agriculture include:
1. Biofertilizers: Engineered microorganisms help plants absorb nutrients more effectively, reducing the need for synthetic fertilizers.
2. Biopesticides: Biologically-derived pesticides control pests without harming the environment, providing a sustainable alternative to chemical pesticides.
3. Lab-Grown Meat and Plant-Based Proteins: Synthetic biology is behind innovations in alternative proteins, such as lab-grown meat and plant-based substitutes, reducing the need for traditional animal agriculture and helping lower greenhouse gas emissions.
Biotechnology is creating sustainable solutions that reduce environmental impact and help agriculture adapt to changing demands and environmental conditions.
Conclusion
Innovations and new technologies are transforming agriculture, offering sustainable and efficient solutions to meet the challenges of modern farming.
From precision agriculture and AI to blockchain and biotechnology, these advancements empower farmers to increase productivity, reduce environmental impact, and improve food security. As these technologies continue to evolve, they promise a future where agriculture is not only more resilient and profitable but also plays a vital role in addressing global issues like climate change, resource conservation, and food security.
By embracing these innovations, the agricultural industry can ensure it meets the demands of the 21st century while safeguarding the planet for future generations.

